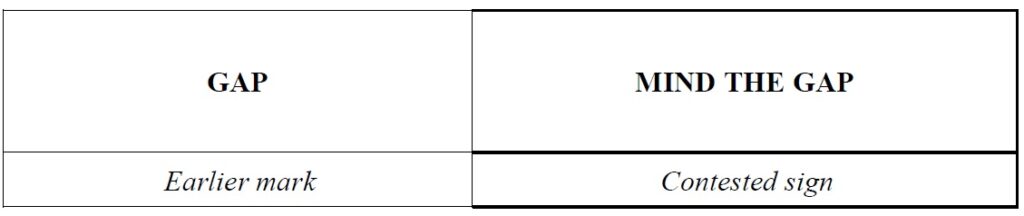
Visually and aurally, the contested sign incorporates the sole element constituting the earlier mark. This element is distinctive, regardless of whether it will be understood or not. Therefore, the signs share the coinciding letters ‘GAP’ and their sounds, while they differ in the elements ‘MIND’, which is also distinctive, and ‘THE’, which only has a low degree of distinctiveness.
Conceptually, the signs are similar to an average degree for the part of the relevant public who understand the coinciding element ‘gap’ in both signs, regardless of whether the contested sign would be perceived as an expression as a whole or not. It is clear that the warning relates to the presence of a ‘gap’, so that this coinciding element does not lose its meaning within the expression.
EUIPO > Opposition > Board of Appeal > Case R 1355/2024-4, on 27 August 2025
□ non-hypothetical:現実の、仮ではない(⇔hypothetical)
□ undue profit:不当利得
□ coinciding:一致する、同時発生する
□ warning:警告、注意、予告
□ presence:存在、出席、面前
「GAP」ブランドの名声から不当利益を得る現実的な将来リスク -1
外観及び称呼上、被異議商標は、先行商標を構成するだた一つ要素を含んでいる。当該要素は、(その意味が)理解されるか否かを問わず、自他商品識別力を有する。したがって、両商標は、「GAP」の文字及びその称呼を共通にする一方、識別力を有する文字要素「MIND」、及び、識別力の程度が低い文字要素「THE」において相違する。
観念において、被異議商標が全体として一つの用語と認識されるか否かを問わず、両商標に共通する「gap」の文字要素を理解する需要者の間で、両商標は平均程度に類似する。明らかに、「gap」(すき間・隔たり)の存在に関連する警告であることから、両商標に共通する当該要素は、被異議商標の構成中においても、その意味を失っていない。

the warning relates to the presence of a ‘gap’, so that this coinciding element does not lose its meaning within the expression
「GAP」がアパレルブランドとして有名であるとしても、そもそも、「GAP」の語は辞書に掲載された既存語であり、辞書掲載の意味合いを有していることからしますと、「MIND THE GAP」の文字から「GAP」ブランドが想起されるのか、甚だ疑問です。欧州連合では、日本人の想像以上に、EU加盟国ごとに、言語に対する認識の違いがあるようです。



