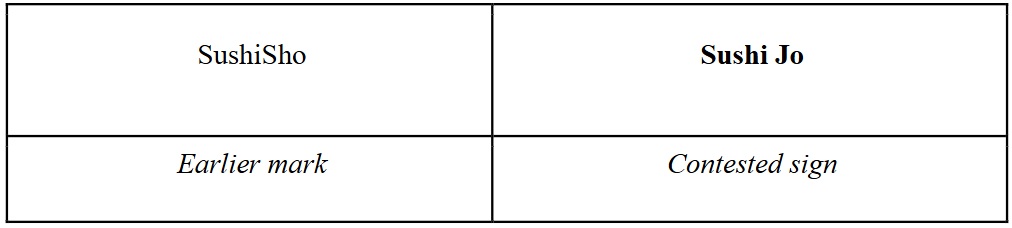
While both signs feature a distinctive verbal element, namely ‘Sho’ (in the earlier mark) and ‘Jo’ (in the contested sign), which both end with the letter ‘o’, they differ in their initial letters (‘Sh’ vs. ‘J’) and in length (3 letters vs. a space followed by 2 letters).
Aurally, they differ in the pronunciation of the elements ‘Sho’ and ‘Jo, which will be pronounced by the public in the relevant territory as /SHO/ and /YO/, respectively. Therefore, when pronounced, the differences between the signs are clearly perceptible.
Even though both marks share the same initial element, this factor carries less weight in assessing the similarity of these signs. In light of the case-law, the similarities and differences between the only distinctive components of the opposing marks are given greater consideration.
EUIPO > First Board of Appeal > 05/12/2025, R605/2025-1, Sushi Jo / SushiSho
□ feature:(目立つ特徴として)備える・もつ、含む
□ end with ~:~で終わる
□ respectively:それぞれ、各々、個々に
□ perceptible:知覚できる、感じ取れる
□ carry less weight:影響力(重み)がない・持たない、重要でない
共通文字「Sushi」は、指定商品・役務の記述表示 - 2
両商標とも、自他識別力を有する文字、すなわち、先行商標が「Sho」、本件商標が「Jo」、を含んでおり、いずれも欧文字「o」で終わるが、語頭文字(ShとJ)、及び、文字数(3文字と空白の後に2文字)が異なる。
称呼上、関連地域の公衆が、それぞれ「SHO」、「YO」と発音する「Sho」と「Jo」の文字部分において、両商標の発音は異なる。したがって、両商標の称呼の相違は、明確に認識できる。
語頭文字が一致しているとしても、両商標の類似性を評価する上で、当該要素は重要ではない。判例法に照らせば、対立する商標の構成要素のうち、識別力を有する部分同士の類似点と相違点が、より重視される。

the similarities and differences between the only distinctive components of the opposing marks are given greater consideration.
「SushiSho」と「Sushi Jo」。これだけを見れば、非常に紛らわしい印象を受けますが、商標の類否においては、自他識別力のある部分が重視されます。自他識別力をある部分というのは、商標として機能する、すなわち、特定の事業者の商品や役務を表示する役割を発揮する部分のことです。「Sushi」の文字を見て「寿司」を思い浮かべるとしても、この文字だけで、どの事業者の指すのか、全く理解できません。このため、「Jo」と「Sho」の部分のみを抽出・対比して、商標の類否を判断します。



